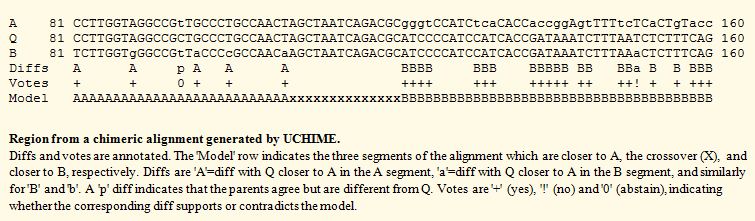
| See also uchime_ref command uchime_denovo command UCHIME in practice Chimera formation Amplicons Abundance estimation UCHIME order dependency Reproducibility of results Comparison of UCHIME and DECIPHER Downloads Please note: I now consider de novo UCHIME obsolete for OTU clustering pipelines because UPARSE is a superior approach.. About UCHIME The fundamental step in UCHIME is a search for a 3-way alignment of a query sequence with two parent sequences (A and B) such that one parent is more similar to one segment of the query (Q) and the other parent is similar over another segment, as in the figure below. A score is calculated from the alignment. Higher scores indicate a stronger chimeric signal. A score cutoff set by the ‑minh option (0.28 by default) determines whether the query is classified as a chimera.
This search can be performed with a reference database of parent sequences provided by the user, or the database can be constructed de novo from the query sequences. In de novo mode, parent sequences are assumed to be more abundant than their chimeras because the parent amplicons will have undergone more rounds of amplification. Parameter tuning Reference database mode De novo mode >FQ23BBGZ5;size=23; The minimum abundance skew is specified by the ‑abskew parameter, which defaults to 2.0 (because one round of PCR doubles the abundance). Abundance is a measure of how many amplicons with a given unique sequence were present in the sample after amplification by PCR. One way to estimate this is to sum the total number of reads in the cluster used to estimate the given amplicon sequence. UCHIME uses only ratios of abundances, so the absolute value does not matter. However, using the number of reads is a useful indicator—for example, a cluster containing one read is likely to be spurious. Amplicon sequences and abundances can be estimated using USEARCH, or by using another algorithm such as Chris Quince's PyroNoise or AmpliconNoise. When using de novo mode, sequences should be estimated amplicons from one sequencing run (strictly, one PCR amplification stage), otherwise abundances may not be directly comparable.
Reference |