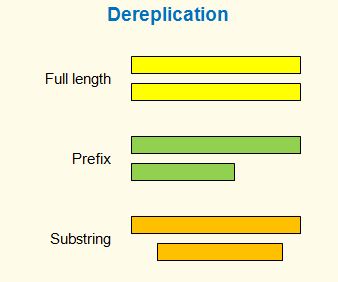
| Dereplication is the identification of unique sequences so that only one copy of each sequence is reported. USEARCH supports dereplication with the derep_fulllength and derep_prefix commands. See also Different definitions of duplicate sequences are possible, as shown in the figure.
The full-length definition is the easiest to understand and also the easiest to implement in an algorithm: if two or more sequences are identical, all except one are kept, for example: A = GATTACA With prefixes, a sequence A is discarded if it is a prefix of some other sequence B in the set, for example: A = GATTAC With substrings, a sequence A is discarded if it is a substring of some other sequence B, for example: A = -ATTAC- All prefixes are substrings, and full-length matches are both prefixes and substrings. So: substrings >= prefixes >= full length matches. USEARCH supports full-length
and prefix dereplication, but currently not substring. In
next-generation sequencing applications, prefix dereplication is
useful for quality-trimmed reads, which are often truncated at
their right-hand end where quality scores tend to fall, but rarely
if ever at their left-hand ends. So far, I haven't come across a
case where substring dereplication is needed -- if you know of one,
please let me know. |