Top-hit identity distribution
See also
Cross-validation by identity
usearch_global command
A top-hit identity distribution (THID) is useful for visualizing distances between a set of query sequences, e.g. OTUs, and a reference database used to predict a trait, e.g. an RDP Classifier training set. OTUs with low identities create a challenging problem for prediction algorithms. Reviewing a THID for a set of OTUs gives an indication of whether predictions based on a given reference are likely to be robust.
USEARCH does not currently support generating a THID as an image file; if this would be useful for you, please let me know . However, it is straightforward to make one with the help of a small script.
Run the OTUs against the reference using the usearch_global command , e.g.:
usearch -usearch_global otus.fa -db refdb.fa -strand plus -id 0.5 \
-maxaccepts 8 -maxrejects 128 -top_hit_only \
-userout hits.txt -userfields query+target+id
Write a script to scan hits.txt. For each hit, round identity to the nearest integer. Count the number of hits for each identity value. Write the counts to a tabbed file and generate a histogram. The example below is a THID for OTUs from a soil sample, colored to indicate the most probable lowest common rank with the NCBI BLAST 16S reference database.
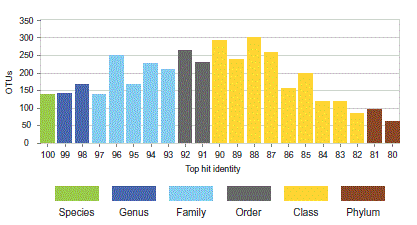
References (please cite)
R.C. Edgar (2018), Accuracy of taxonomy prediction for 16S rRNA and fungal ITS sequences, PeerJ 6:e4652
• Cross-validation by identity, novel benchmark strategy enabling realistic accuracy estimates
• Genus accuracy of best methods is 50% on V4 sequences
• Recent algorithms do not improve on RDP Classifier or SINTAX
R.C. Edgar (2018), Taxonomy annotation and guide tree errors in 16S rRNA databases, PeerJ 6:e5030
• Approx. one in five SILVA and Greengenes taxonomy annotations are wrong
• SILVA and Greengenes trees have pervasive conflicts with type strain taxonomies

